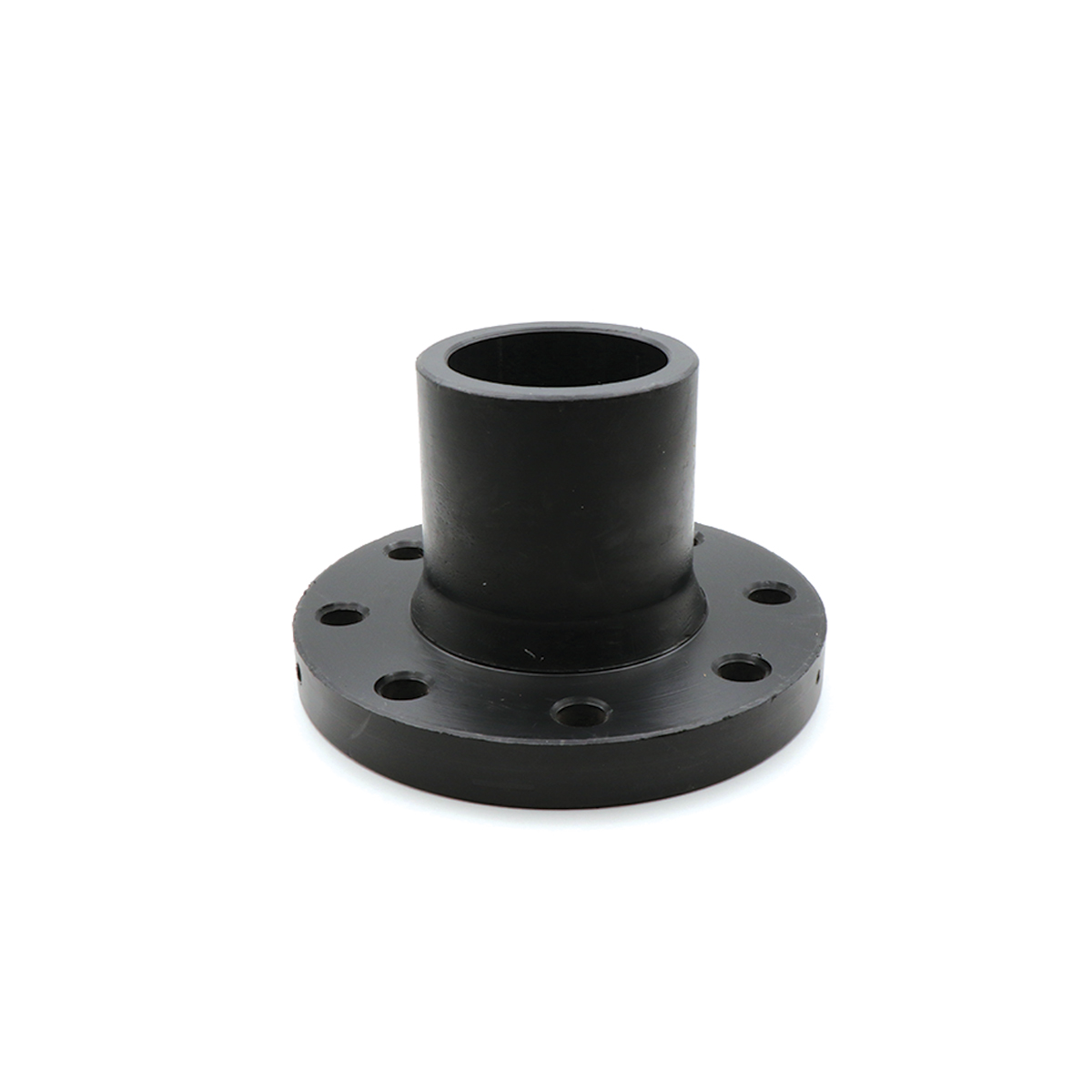
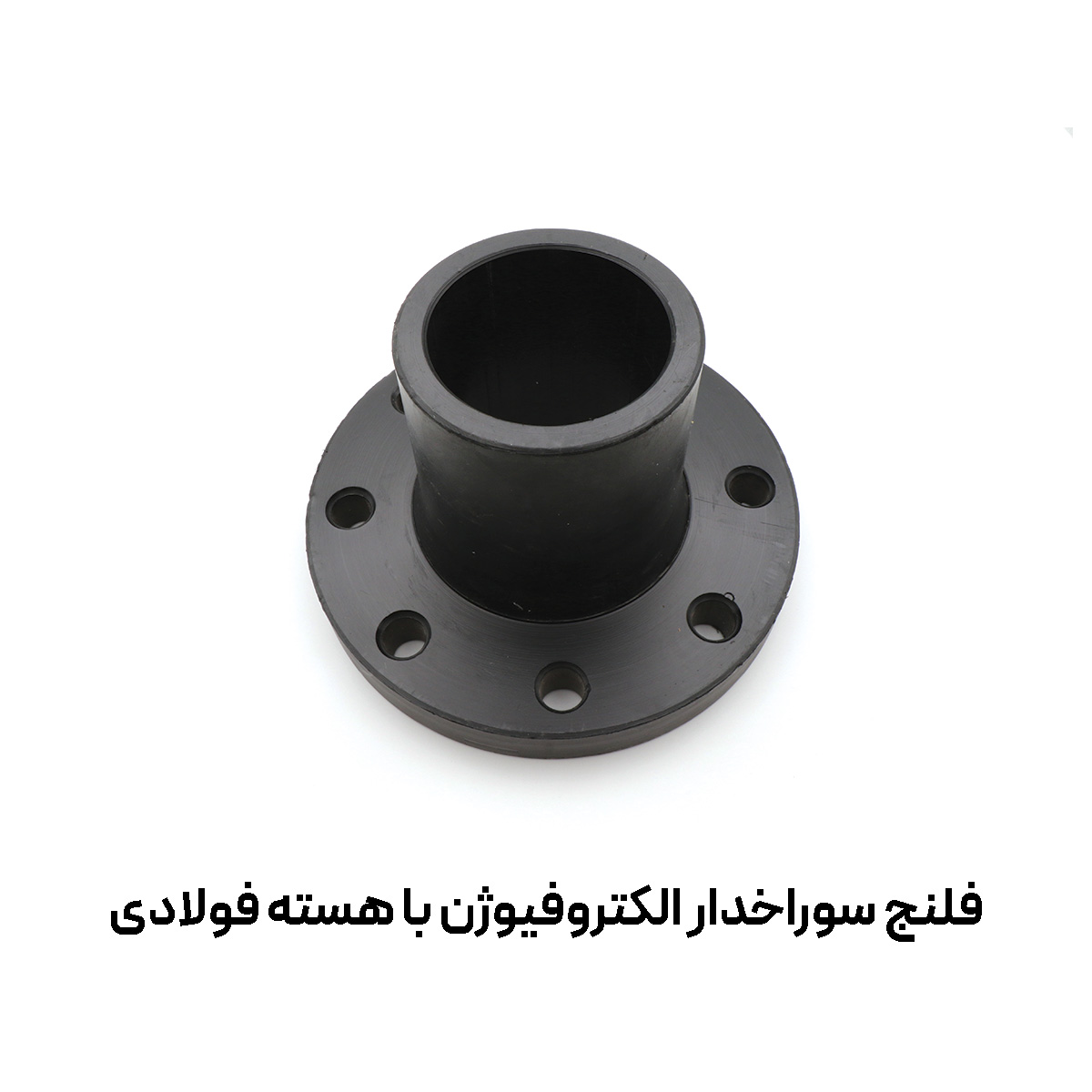
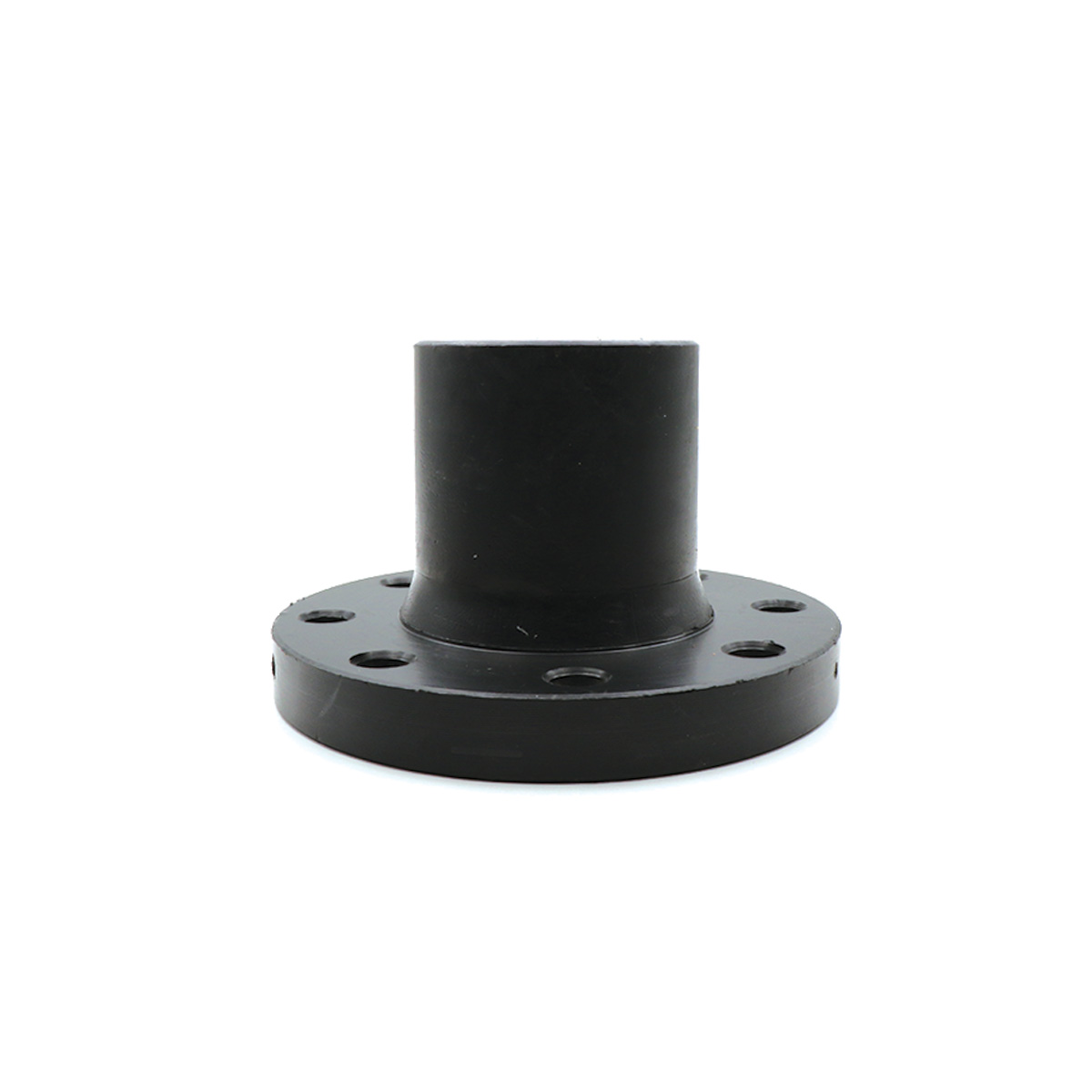
Electrofusion drilled flange with a steel core is an integrated solution for creating a dependable flanged connection between polyethylene pipes and metal equipment. The smart combination of a PE100 body and a precision-machined steel ring delivers high mechanical strength while enabling reliable sealing and fast installation—especially on water lines, wastewater networks, pressurized irrigation, and pump circuits where prolonged downtime is costly.
What Is an Electrofusion Drilled Flange?
In this connection, a robust steel ring is embedded inside the polyethylene body, and the electrofusion heating coil creates a molecular bond between the fitting body and the PE pipe. The result is a joint that:
- Provides a standard flange drilling pattern and easily bolts to valves, pumps, tanks, and metallic equipment.
- Requires no separate backing ring, which speeds up installation and improves alignment.
- Keeps the metal surface isolated from environmental corrosion with full polyethylene coverage.
Benefits and Practical Value
- Fast, simple installation: Only bolts/nuts and an electrofusion machine; no complex tooling.
- High mechanical strength: The steel core carries bolt loads and tensile forces.
- Chemical and corrosion resistance: PE100 body and full coverage over the core improve durability in wet and corrosive environments.
- Lower scaling and pressure drop: Smooth PE internal surfaces reduce deposition.
- Outdoor resilience: UV and impact resistance for above-ground projects.
- Removable and reusable: If designs change, unbolt and redeploy the part easily and cost-effectively.
General Specifications and Technical Range
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Nominal size (DN) | 63 to 400 mm |
| Body/connection standard | Electrofusion body following DIN practices for PE fittings |
| Flange drilling pattern | PN10/PN16 per EN 1092-1 / DIN 2501 |
| Core material | Carbon steel ST37 / S235JR, precision-machined |
| Body material | UV-stabilized HDPE PE100 |
| Pipe SDR compatibility | SDR11 and SDR17 (per manufacturer guidance) |
| Sealing method | Elastomeric gasket compatible with the fluid (EPDM/NBR) |
| Typical service temperature range | Municipal water and irrigation within ambient temperatures (per manufacturer datasheet) |
| Recyclability | Disassembly and reuse enabled by bolted connection |
Applications
- Quick connection/disconnection of pumps, gate valves, check valves, and instrumentation.
- Transition between PE pipe and metallic equipment at pump stations and tanks.
- Water supply and sewer networks, pressurized irrigation lines, and mining/process industries with moderate corrosivity.
- Locations requiring periodic access for service or calibration.
Quick Comparison of Flanged Connection Options
| Comparison index | Electrofusion drilled flange (steel core) | PE welded flange + loose backing ring | All-metal coated/mechanical flange |
|---|---|---|---|
| Installation speed | High | Medium | Medium |
| Need for backing ring | No | Yes | No |
| Corrosion resistance | Very good (protected core) | Good | Medium; needs coating/paint |
| Initial cost | Medium | Medium to high | Variable |
| Life-cycle cost | Low | Low | Higher (anti-corrosion upkeep) |
| Installation error risk | Low to medium | Medium | Low to medium |
| Reusability | Yes | Limited | Yes |
Step-by-Step Installation Guide (Best Practice)
- Pipe cutting & prep: Square cut, deburr, and clean.
- Surface peeling: Remove the oxidized/contaminated layer with a proper scraper to expose a fresh, uniform surface.
- Final cleaning: Use lint-free wipes and isopropyl alcohol; avoid touching with bare hands.
- Insertion depth marking & alignment: Secure the pipe in a stress-free position.
- Positioning & fixturing: Seat the flange on the pipe and clamp the assembly with dedicated fixtures to eliminate play.
- Electrofusion welding: Set the machine per barcode/manufacturer parameters and complete the fusion cycle; apply no loads until full cooling.
- Bolting: After full cooling, tighten in a cross pattern in 2–3 passes to the recommended torque; use suitable washers.
- Final inspection: Check alignment, sealing (Leak Test), and fusion indicator pins.
Design and Selection Notes
- Working pressure & flange class: Choose PN10/PN16 to match network pressure and the mating equipment.
- Chemical compatibility: Select gasket and body with regard to the fluid (water, wastewater, dilute chemicals).
- Pipe SDR & tolerances: Verify diameter, ovality, and SDR compatibility with the electrofusion coupling.
- Environmental conditions: For outdoor installs, consider mechanical protection against impact and direct sun.
- Alignment & stress control: Use proper supports so thermal and vibrational loads are not transferred to the joint.
Periodic Maintenance and Inspection
- Routine visual checks for leakage, bolt condition, and gasket health.
- Staged re-tightening for thermal/vibratory services (per manufacturer instructions).
- Avoid direct impacts and chemicals that degrade gasket elastomers.
Common Mistakes and Prevention
- Insufficient surface prep: Leads to poor fusion; perform proper peeling and cleaning.
- No clamping: Causes irregular fusion and leakage; fixturing is essential.
- Loading during cooling: Reduces fusion strength; avoid any stress until the specified cooling time elapses.
- Incorrect bolts: Excess length or improper grade can damage the core and sealing; use standard bolts/nuts with flat washers.
Sustainability Considerations
The polyethylene body’s inherent corrosion resistance and the bolted, demountable design reduce repair and replacement costs over the service life. Reusability also minimizes project waste.
About Tamam Baha
As a supplier of electrofusion drilled flanges with steel cores, Tamam Baha provides common sizes (DN63 to DN400) and application-focused technical guidance on pressure class, gasket selection, and installation requirements—helping engineering teams choose the right option for their project’s operating pressure, fluid, environment, and maintenance plan.