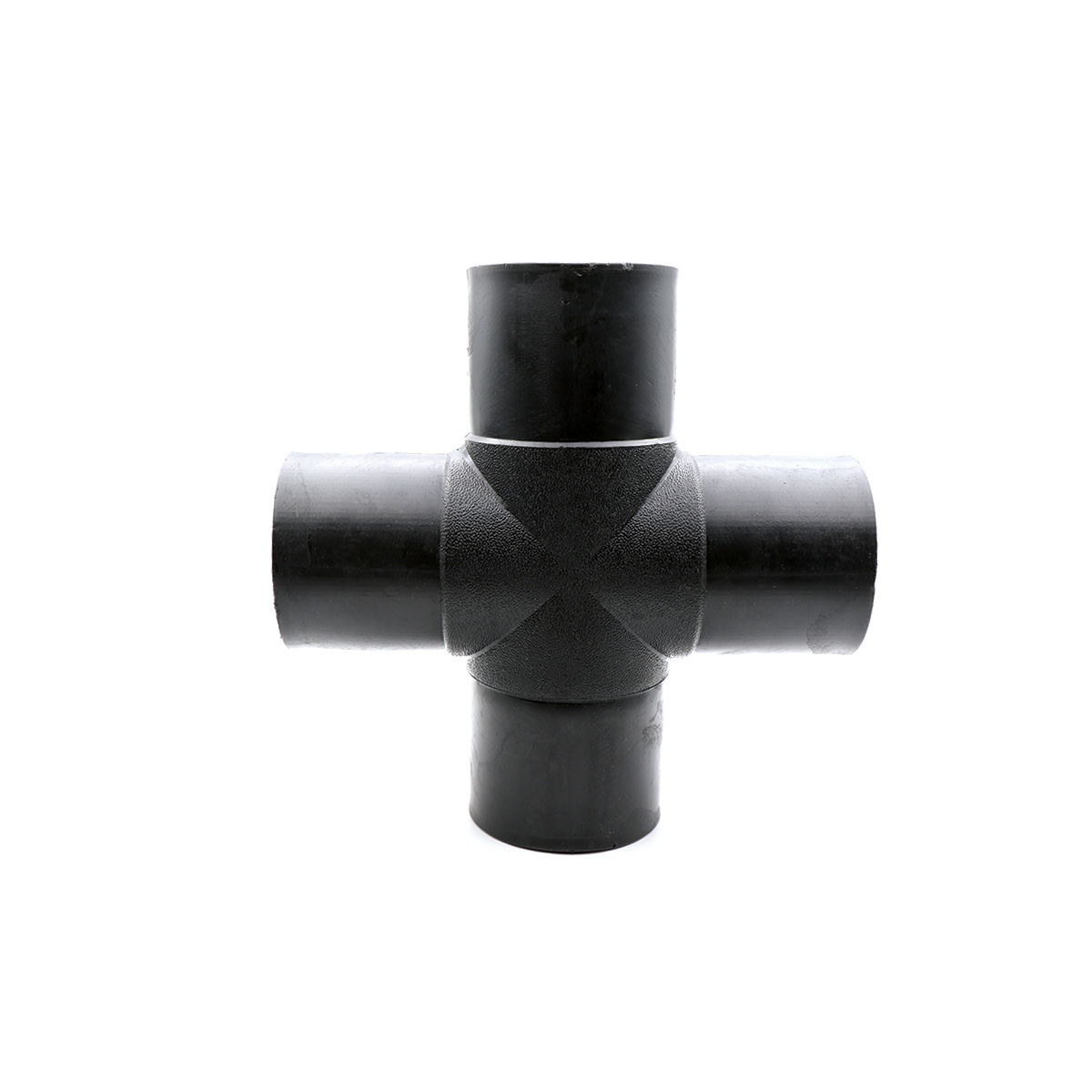
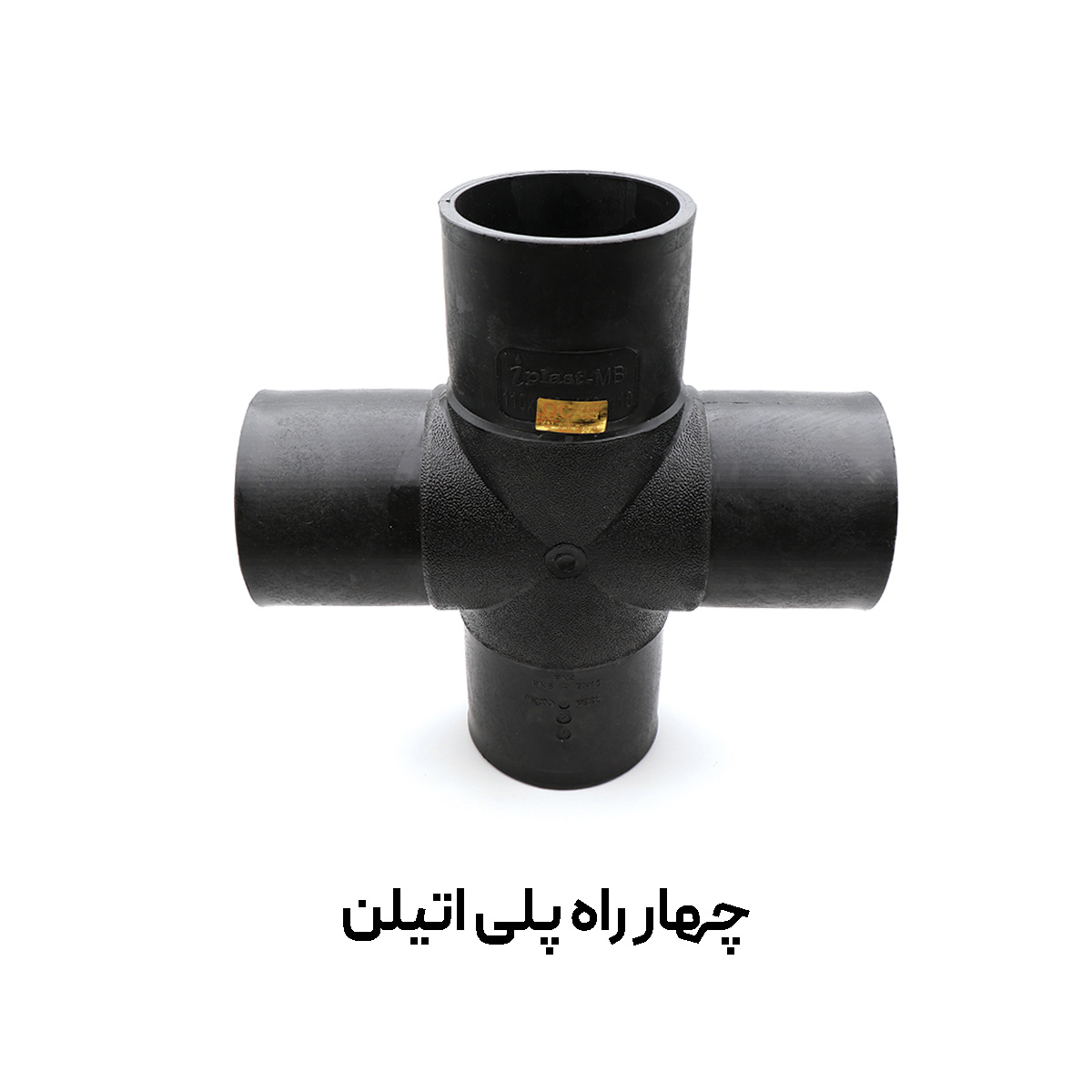
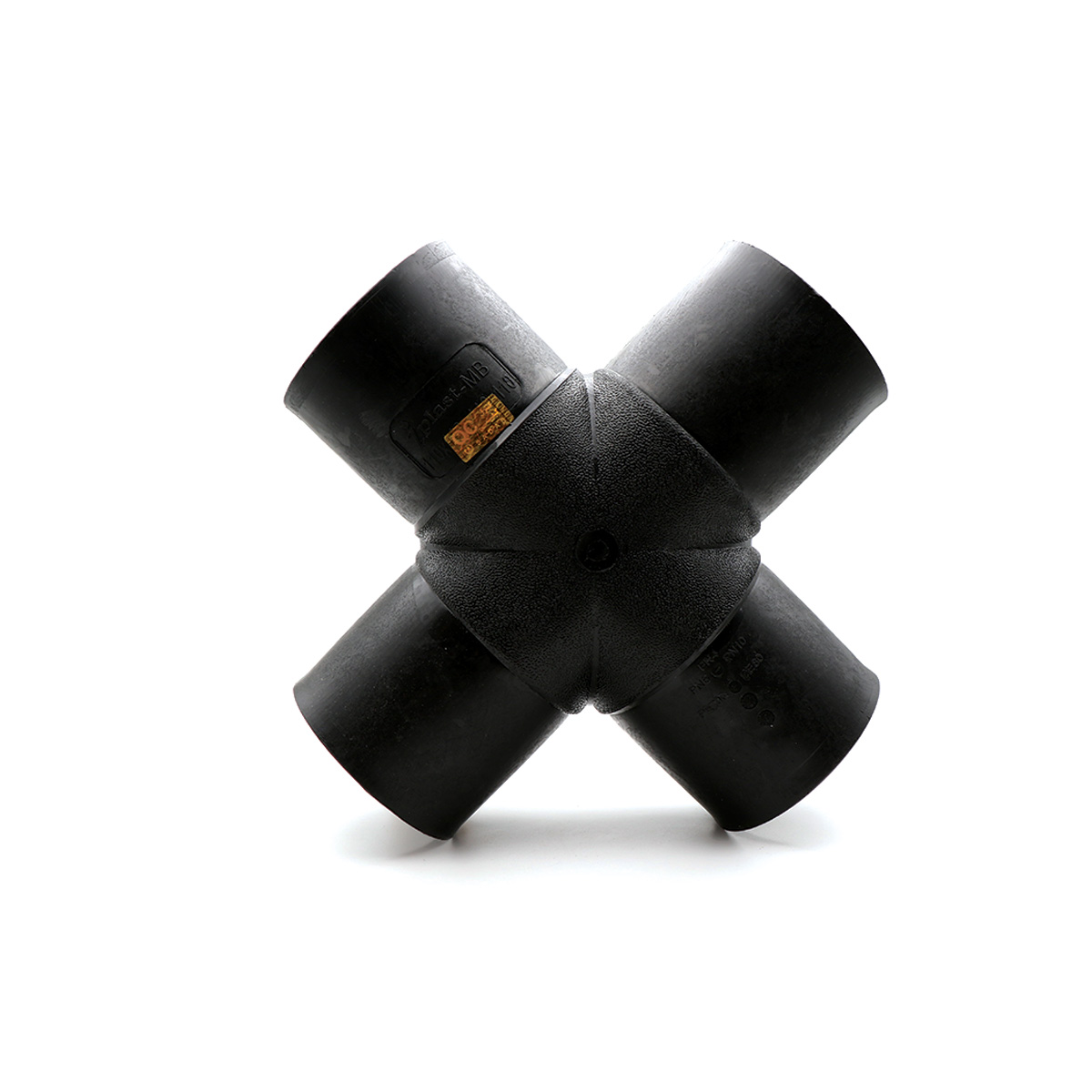
A polyethylene butt-weld cross (Cross) is one of the key fittings in piping networks, used to take simultaneous branches from four directions at 90° angles. The part is produced with PE100 material grade, standard black color, and UV stability, and is offered in common sizes from 63 to 400 mm. Connection is primarily by butt-fusion welding, and, when needed, compatibility with electrofusion fittings is foreseen.
Standards and Quality Control
Polyethylene butt-weld crosses are manufactured and tested in accordance with national and international requirements, including:
- INSO 14427-3 (national equivalent for polyethylene fittings)
- DIN 16963 (dimensional guidance and fitting requirements)
- ISO 4427 (polyethylene piping systems for water supply)
Quality control includes dimensional checks, hydrostatic pressure testing, thermal reversion, oxidation induction time (OIT), and visual inspection of the weld surface.
Manufacturing and Joining Methods
- Fabrication from pipe: Components are prepared from PE100 pipe with 45° cuts and then butt-fused together. Common for large sizes and special projects.
- Part-making/machining: In some sizes, the cross body is produced by injection molding or machined from a preform.
- Field joining methods:
- Butt Fusion for direct connection of the cross to the pipe.
- Electrofusion when reinforced couplers or alignment correction are required.
Flatness of surfaces, alignment, plate temperature, pressure, and hold time must be controlled per the welding procedure.
Key Technical Specifications
- Material: High-density polyethylene PE100, UV-stabilized.
- Color/Marking: Black body; blue stripe for water supply, yellow stripe for gas (on request).
- Common SDR classes: SDR11, SDR13.6, SDR17.
- Typical working pressure: Up to PN16 for water at 20 °C (depending on SDR and design).
- Operating temperature range: Generally temperate; increase in temperature requires derating of allowable pressure.
- Internal surface: Smooth, low roughness to reduce pressure drop and fouling.
Advantages
- High flexibility and absorption of vibration/loads from soil settlement and earthquakes
- Uniform weld bead and reliable sealing when executed correctly
- Excellent resistance to moisture, corrosion, and common chemicals
- Low weight, easy handling, and fast installation
- Reduced flow noise and low headloss due to low roughness
- Durable outdoors with UV-stabilized products
Limitations and Design Considerations
- Pressure: Most designs cover pressures up to about PN16; higher pressures require a more suitable SDR class or alternative material.
- Temperature: Not suitable for very hot fluids; increase in temperature requires pressure derating.
- Chemical compatibility: Not suitable for oily/aromatic hydrocarbon solutions. Contact with petroleum derivatives requires manufacturer approval and compatibility review.
- Welding execution: Final quality depends entirely on calibrated equipment and trained operators.
Applications
- Urban and industrial pressurized water supply networks
- Firefighting systems and ring mains
- Gas distribution lines (subject to relevant SDR classes and requirements)
- Agricultural irrigation and drip/sprinkler networks
- Transfer and collection of domestic and industrial wastewater (medium pressure)
- Process, power, and petrochemical industries for cooling water, effluent, and compatible fluids
Guide to SDR Selection and Nominal Working Pressure
The following values are for PE100 at a reference temperature of 20 °C and may vary according to project standards.
| SDR rating | Nominal working pressure (PN) | Suggested applications | Design note |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDR11 | PN16 | High-pressure water supply, gas, fire rings | Stiffer with lower bending deflection |
| SDR13.6 | PN12.5 | General municipal/industrial water supply | Balanced weight and strength |
| SDR17 | PN10 | Irrigation and medium-pressure sewage | More economical, greater flexibility |
Note: For temperatures above 20 °C, reduce allowable pressure according to derating tables.
Nominal Sizes of Equal PE Cross (Zk and Le Dimensions)
| Nominal size (mm) | Zk (mm) | Le (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 63* | 106 | 60 |
| 75* | 124 | 72 |
| 90 | 136 | 70 |
| 110 | 165 | 85 |
| 160 | 206 | 101 |
| 200 | 246 | 118 |
| 250 | 303 | 144 |
| 315* | 299 | 125 |
| 355* | 325 | 125 |
| 400* | 325 | 125 |
Installation and Execution Notes
- Precise beveling and cleaning of contact surfaces before welding
- Full alignment of pipes and cross; use holding clamps
- Control of plate temperature, contact time, and holding pressure per procedure
- Cooling under no-stress conditions; do not move until cooling is complete
- Perform hydrostatic testing before commissioning and insulate buried sections
Maintenance and Inspection
- Periodic inspection of welds and supports
- Leak monitoring under operating pressure and after hydraulic shocks
- Prevent contact with incompatible chemicals and direct heat sources
- Record welding data (parameters/operator/equipment) for quality traceability
Buying and Selection Guide
When selecting a polyethylene butt-weld cross, consider:
- Nominal size and compatibility with pipe diameter
- Required SDR/PN based on pressure and temperature
- Manufacturing method (fabricated from pipe or molded part) and quality class
- Need for electrofusion compatibility for specific connections
- Standards certificates and test reports from the manufacturer
- Installation environment (buried/exposed, sunlight, ambient temperature)
Tamam Baha, as a supplier of PE100 polyethylene butt-weld crosses, can provide a wide range of sizes, SDR classes, and custom fabricated builds to project drawings. Relying on a trusted supply network, pre-purchase technical advice, test certificates, and coordinated quick dispatch, it aims to support your timelines. While Tamam Baha is not the only seller of these products, it strives to be a reliable and cost-effective option for water, irrigation, gas, and process-industry projects across the Middle East.