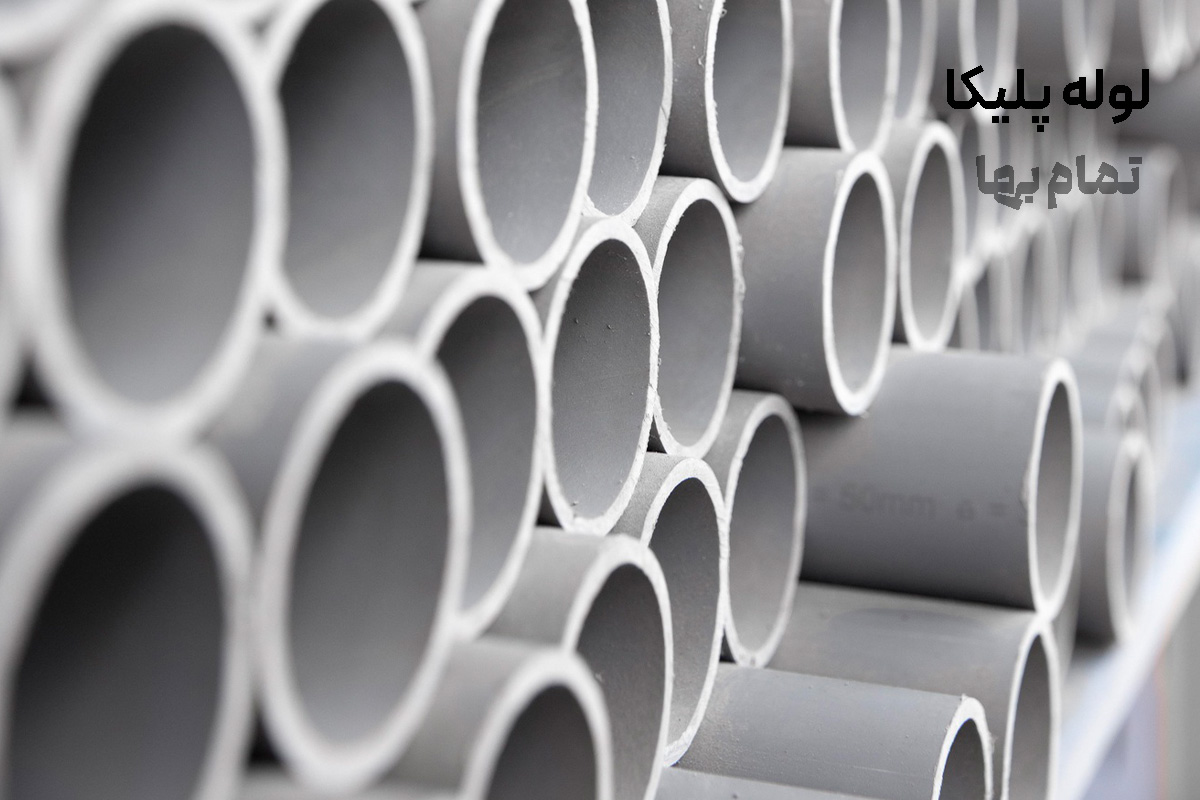
PVC pipe (“Polika”) in Iran’s building and infrastructure sector is regarded as the backbone of fluid networks and cabling; a pipe made of unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (PVC-U). Because the earliest products entered the market under the “Polika” brand in the 1970s, the trade name quickly displaced the scientific term and, in consumers’ minds, has become synonymous with any kind of PVC pipe. This article serves as a “reference content,” taking a comprehensive look at Polika pipes—from material chemistry and production standards to network design, joining, installation, economic evaluation, and environmental considerations.
Chemical composition and structure
Polika pipe is made from PVC powder with an average molecular weight of 57–70 kDa. Tin (stannate) or calcium–zinc thermal stabilizers, paraffinic lubricants, acrylic processing aids, and mineral fillers (typically calcium carbonate, mesh 1250) are added to the formulation to control rheology, surface smoothness, and shrinkage. The absence of plasticizers (plasticiser-free) yields high stiffness and tensile strength and minimizes chemical permeability.
Classification by pressure class
- Class 4 (light-duty): up to 4 bar at 20 °C, thin wall; suitable for ventilation ducts and rainwater drainage.
- Class 8 (semi-heavy): up to 8 bar; the backbone of domestic sewer networks and cable protection.
- Classes 10 and 16 (heavy-duty): 10 or 16 bar; for agricultural water conveyance, industrial wastewater, and suction lines.
New formulation grades
| Grade | Manufacturing technology | Key feature | Continuous temp (°C) | Typical application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-PVC | No plasticizer | Rigid, impact-resistant | 0–60 | Potable water, sewage |
| O-PVC | Thermo-axial orientation | 2–3× higher impact energy | 0–45 | High-pressure lines up to 25 bar |
| C-PVC | Post-extrusion chlorination | Superior heat resistance | 0–90 | Hot water, heating |
| PVC-Hi | Impact-modified composite | Very low brittle fracture | −10–60 | Gas and compressed air transfer |
Dimensions and specific mass per Iranian National Standard 9119-2
| Outside diameter (mm) | Nominal thickness (mm) | Approx. weight (kg/m) | Pressure class (bar) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 1.6 | 0.30 | 4 |
| 40 | 2.0 | 0.88 | 8 |
| 63 | 2.5 | 1.76 | 8 |
| 110 | 3.2 | 3.95 | 10 |
| 160 | 4.0 | 7.58 | 10 |
| 225 | 6.6 | 18.2 | 16 |
| 315 | 7.9 | 32.6 | 16 |
Mechanical and performance properties
- Average tensile strength 45 MPa and elastic modulus 3 GPa; suitable for direct burial down to 12 m with a sand bedding.
- Excellent chemical resistance to mineral acids, dilute bases, salts, and chlorinated compounds; only strong polar solvents (ketones, tetrahydrofuran) can swell Polika.
- Fire behavior class B1 per DIN 4102; self-extinguishing with limited hydrogen chloride generation.
- Thermal conductivity 0.19 W/m·K (one-eighth of steel pipe), reducing heat loss in warm fluids.
- Axial creep under constant load < 3% over 50 years; expansion joints typically needed only for straight runs longer than 30 m.
Manufacturing process and quality control
Single-screw extrusion with a temperature profile of 165-185-195 °C, two-stage vacuum calibration, 10 °C water-spray cooling, and caterpillar haul-off is the most common method. Sampling every 20 minutes is performed for burst-pressure and Gardner impact tests. Newer lines feature online laser diameter gauges and sonic defect detection so wall-thickness deviation beyond ±5% is rejected immediately.
Strategic applications
- Domestic and municipal sewer networks: a fully smooth inner surface (hydraulic roughness k≈0.01 mm) minimizes deposits and enables gravity flow without clogging.
- Pressurized piping: in drip or sprinkler irrigation, Class 10 Polika is a cost-effective alternative to high-pressure polyethylene.
- Power-cable and fiber-optic conduits: excellent dielectric properties (relative permittivity 3.5) and resistance to termites and rodents.
- Guttering and ventilation: lightweight and fast to install, widely used in towers and industrial sheds.
- Chemical and oil & gas services: transfer of brine solutions, acidic refinery effluents, and chemical-injection lines in oilfields.
Hydraulic design principles
- Recommended maximum velocity: 2 m/s for cold water and 1.5 m/s for gravity sewage.
- Minimum slope of 1–2% on horizontal domestic sewer branches for self-cleaning.
- Pressure drop may be modeled with the Hazen–Williams equation (C = 150 for Polika) or Colebrook–White with ε/D = 0.001.
- Suggested safety margin of 1.25 against operating pressure for buried lines.
Jointing methods and comparison
| Jointing method | Pressure capacity (bar) | Installation speed | Special tools | Disassembly |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC solvent cement | 8 | Medium | Primer & brush | Permanent |
| Push-fit | 6–10 | Very fast | None | Semi-permanent |
| Threaded | 10 | Slow | Die set | Releasable |
| Flanged | 16 | Medium | Torque wrench | Easy |
| Electrofusion | 25 | Slow | Fusion unit | Permanent |
Installation and maintenance notes
- Bedding must be free of stones > 20 mm; use 0–4 mm sand with at least 90% Proctor compaction.
- Minimum allowable bend radius is 35× outside diameter. Sharp bends concentrate stress and cause micro-cracks.
- Perform a tightness test 24 h after installation at 1.5× operating pressure; allowable drop is 2%.
- Robotic CCTV inspection every three years in municipal sewers helps prevent early blockages.
Price-influencing factors
- Virgin-resin content: low-cost pipes often contain recycled PVC and > 30% filler; this reduces impact strength and pressure tolerance.
- Actual wall thickness: cutting just 0.1 mm from a 110 mm pipe saves ~4% material but can reduce service life by up to 15%.
- Currency fluctuations and global ethylene prices: directly affect the cost of PVC grade S65.
- Brand and certification: products with traceability codes and ISIRI marking are typically 10–15% pricier but include a five-year warranty.
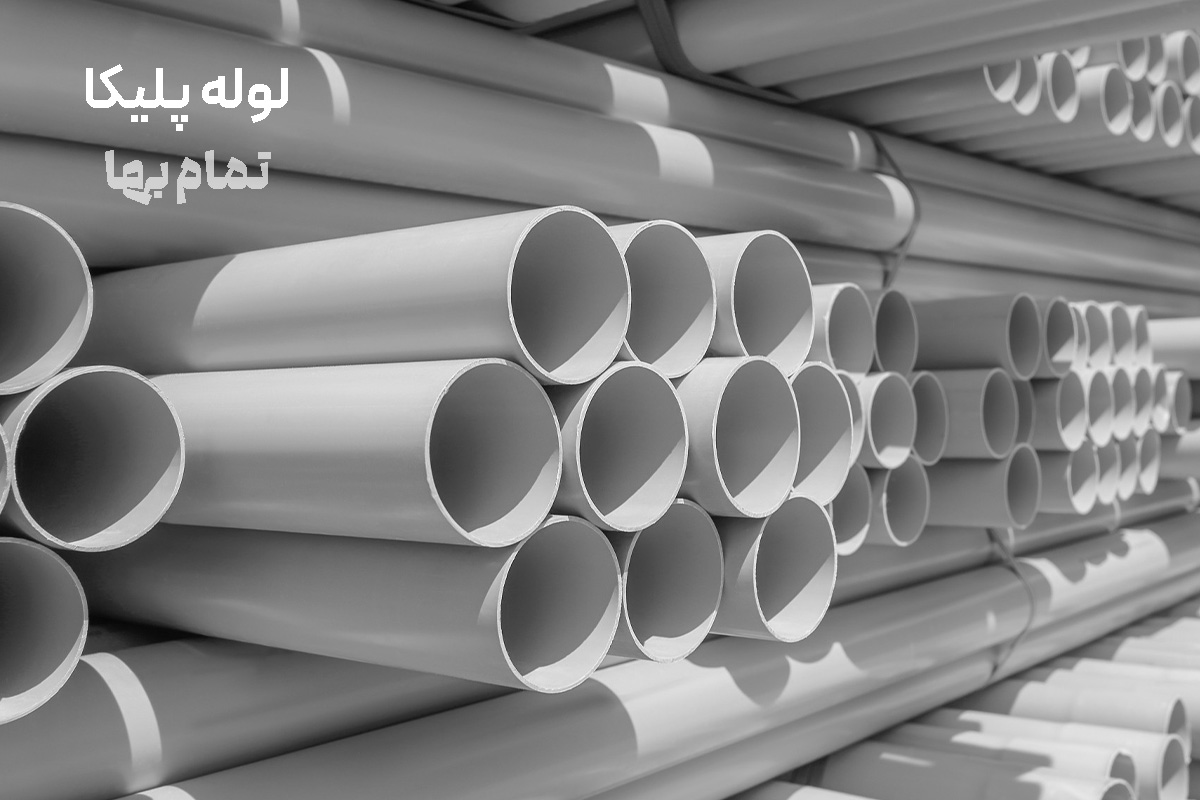

Identifying a standard-compliant pipe
- Uniform gray color without black streaks or excessive gloss.
- A clear, glassy ring when tapped (indicates high density).
- Laser marking every meter showing manufacturer, diameter, pressure class, date, and production shift.
- Passes a 1 kg hammer-impact test at 0 °C without failure.
Environmental considerations and recycling
PVC is recyclable; in its second life it is reused as rigid granules for window profiles or escalator components. Decomposition time in soil exceeds 500 years; therefore, scrap-collection and return-to-process programs are critical. Uncontrolled burning produces HCl and dioxins; sanitary landfilling or mechanical recycling is preferred.
Tamambaha: your trusted partner for Polika pipes
With a nationwide distribution network, “Tamambaha” supplies Polika (PVC) pipes and fittings in all pressure classes and standard sizes. Alongside other reputable suppliers, the store provides official invoices, product-authenticity guarantees, and pre-purchase technical advice—making it easier for contractors, developers, and homeowners to choose the right product, without being tied to a single brand.