Polyethylene rebar, as one of the new branches of non-metallic reinforcement, leveraging long polymer chains and stable carbon–carbon bonds, provides a powerful engineering solution to increase durability and reduce structural weight. This product is based on polyethylenes of different densities (HDPE, LDPE, and in special projects UHMW-PE) and, due to its non-reactive nature, is indifferent to moisture and a wide range of chemicals; hence, in industrial, coastal, subsurface, and even hygienic environments it acts as a substitute for or complement to steel rebar.
Molecular structure and its impact on performance
High-density polyethylene, thanks to low branching, higher crystallinity, and tighter intermolecular spacing, delivers a higher modulus of elasticity and compressive strength than LDPE. In contrast, LDPE—with numerous side branches—has a softer structure and greater bendability. For this reason, engineers often combine the two grades in structures that must absorb impact energy or seismic vibrations to balance stiffness and ductility.
Key features of polyethylene rebar
Chemical and corrosion resistance
Non-metallic bonds and the absence of free metallic ions prevent oxidation and rusting; therefore, it performs reliably in treatment plants, saline irrigation systems, artificial reef beds, and sour-gas pipelines.
Lightweight
The density of polyethylene (0.94–0.97 g/cm³) is roughly one-third that of steel. This advantage not only reduces transportation and handling costs but also lowers dead load, making it ideal for high-rise buildings in seismic zones.
Thermal and electrical insulation
Electrical stability (volume resistivity >10¹⁴ Ω·cm) enables use in power-plant cooling towers, hospitals filled with sensitive equipment, and underground data transmission lines. The low thermal conductivity (≈0.4 W/m·K) also prevents thermal bridging in retaining walls.
Flexibility and impact absorption
Polyethylene rebar endures larger strain before reaching yield; in other words, it stores more elastic energy and prevents brittle failure in concrete or composite elements. This trait is also advantageous in rotating shafts or supports under dynamic loads.
Color spectrum and additives
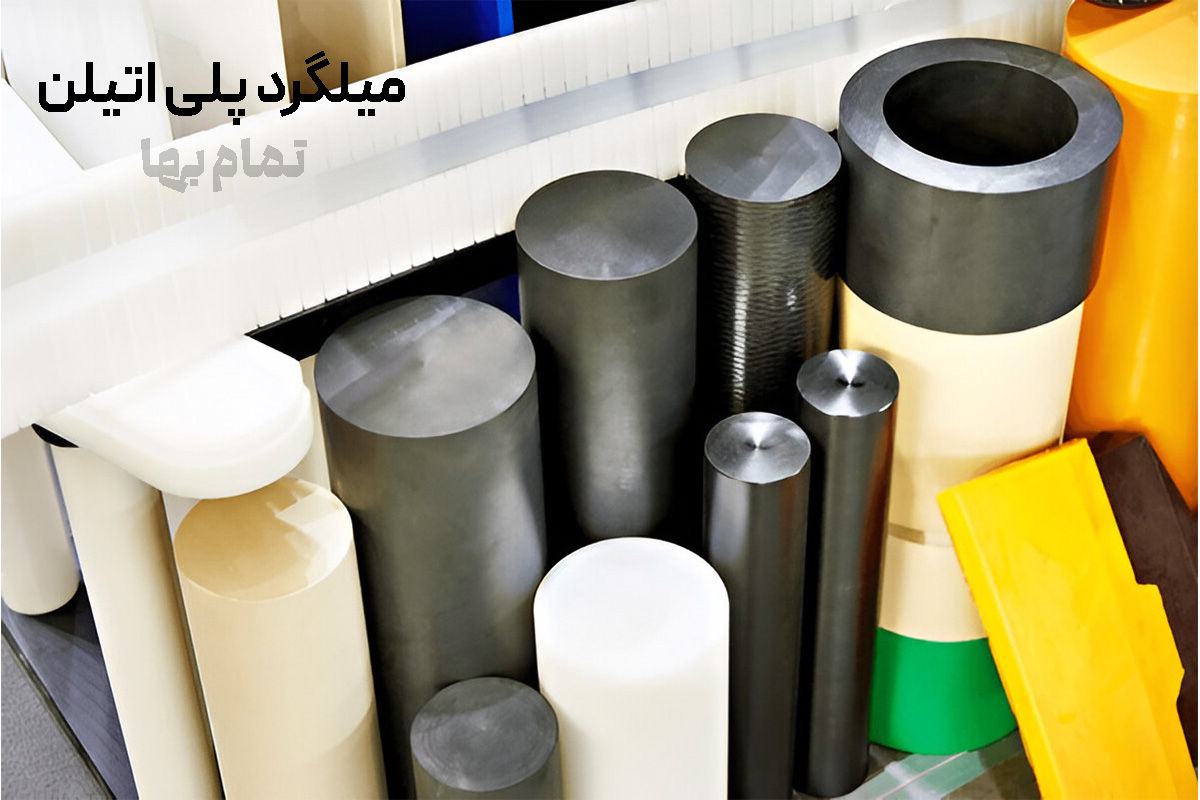
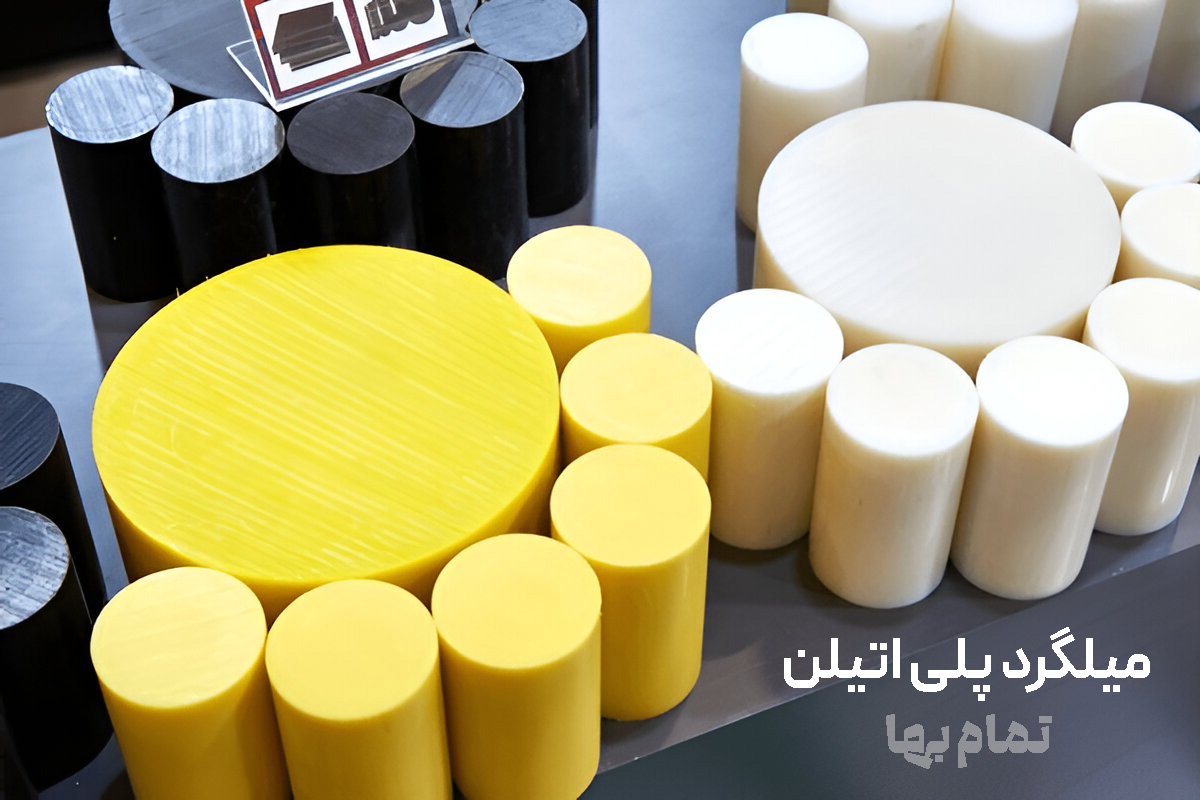
Coloring is not merely decorative; for example, black contains a UV-stabilizer masterbatch, blue indicates potable-water transfer, yellow marks underground gas lines, and white is compounded with food-grade polyethylene. By referring to the color code, the design engineer can quickly identify anti-wear or UV-resistant properties without destructive testing.
Guide table of common HDPE dimensions
| Indicative application | Typical length (m) | Approx. weight (kg/m) | Nominal diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light equipment, MEP installations | 6 | 0.075 | 10 |
| Shear walls and medium frames | 6 | 0.191 | 16 |
| High-stress beams and slabs | 6 | 0.298 | 20 |
| Heavy infrastructural structures | 6 | 0.466 | 25 |
| Large water conveyance lines, breakwater | 6 | 0.764 | 32 |
These sizes are compiled based on common workshop standards in Iran and can be adjusted in special projects according to tensile and creep test results.
Manufacturing process and quality control
- Resin selection – Polyethylene with controlled melt-flow index to prevent internal voids.
- Continuous extrusion – High L/D (~32) extruder screw ensures temperature uniformity.
- Calibration and vacuum bath – Diameter stability keeps ovality below 1%.
- Stepwise annealing – Removes residual stresses and increases fatigue resistance.
- Nondestructive tests – Ultrasonic for internal bubbles, FT-IR spectroscopy for additive composition, and periodic hydrostatic pressure testing.
Weldability and joining methods
- Butt fusion: suitable for diameters 20–120 mm, low cycle time, and joint strength close to 98% of the base material.
- Extrusion fusion: enables filling deep grooves and local in-service repair.
- Electrofusion: coupling with embedded resistance wire, a clean option for confined tunnel spaces.
Installation in composite structures
In polymer concrete or conventional concrete, the anchorage guideline is as follows:
- Embedment depth ≥ 15 × nominal diameter for alternating tensile loads.
- Minimum concrete cover 25 mm near intense heat sources.
- Use epoxy–amine adhesives reinforced with silica filler to improve chemical adhesion.
Performance comparison with alternative rebars
| Rebar type | Corrosion resistance | Relative density | Flexibility | Compressive | Tensile | Brittleness | Relative cost | Indicative applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene | Very high | Low | High | Medium | Medium | Low | Medium | Marine structures, chemical environments |
| Steel | Low | High | Medium | Very high | Very high | Low | Medium | Bridges, piers |
| Fiberglass | High | Very low | Low | Low | Medium | High | Low | Lightweight structures, humid environments |
| Carbon/glass composite | Very high | Medium | Medium | High | Very high | Medium | High | Long bridges, oil-and-gas equipment |
Professional purchasing considerations
- Grade authenticity: obtain melt analysis sheet (MFI, density) and DSC test to confirm crystallinity.
- Project environmental conditions: service temperature, presence of chloride or strong acid, freeze/thaw cycles.
- Approvals and certificates: compliance with ISO 14631 and ISIRI 13301 for hydraulic and impact resistance.
- Vendor technical support: capability for joint-design consulting, adhesive-compatibility evaluation, and providing the correct color code.
Tamam Baha’s specialty store, backed by a wide supply network, offers polyethylene rebars in HDPE and UHMW-PE grades in diverse diameters and colors, and—together with other official distributors in the Iranian market—provides valid laboratory reports, custom cutting, and installation consulting services for civil and industrial projects across Iran.