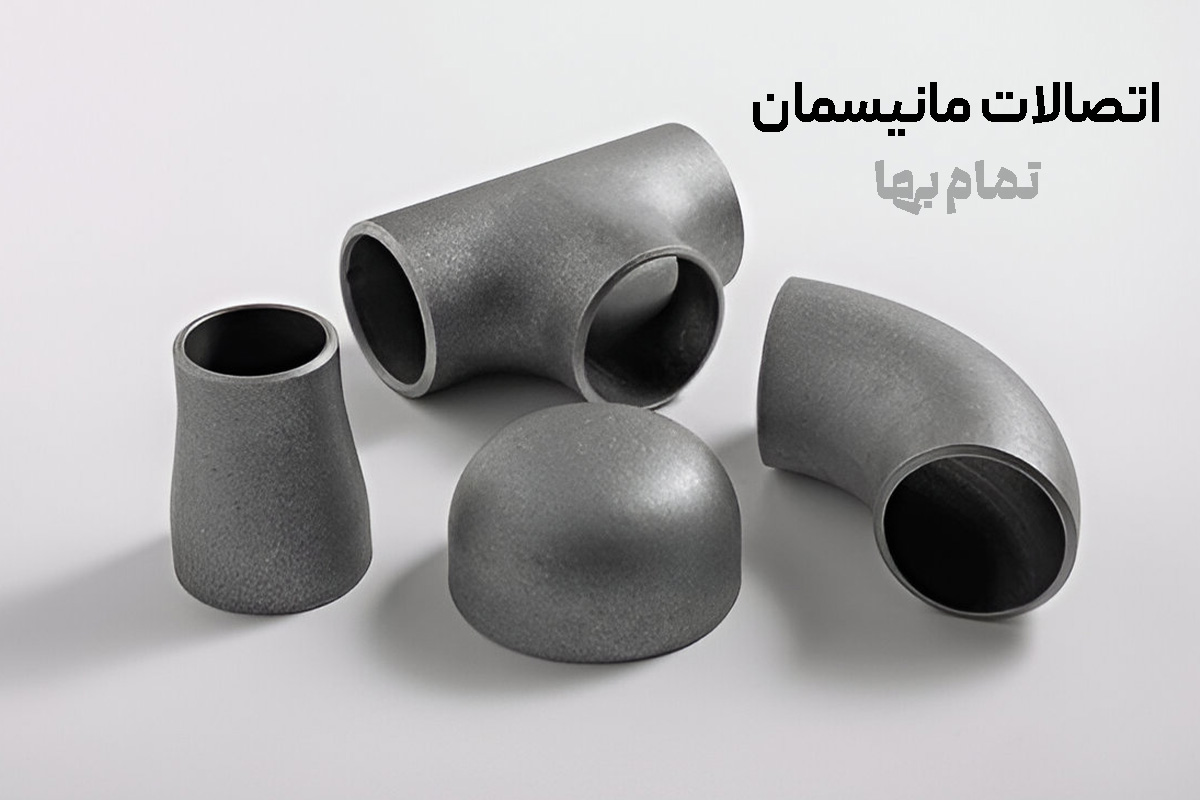
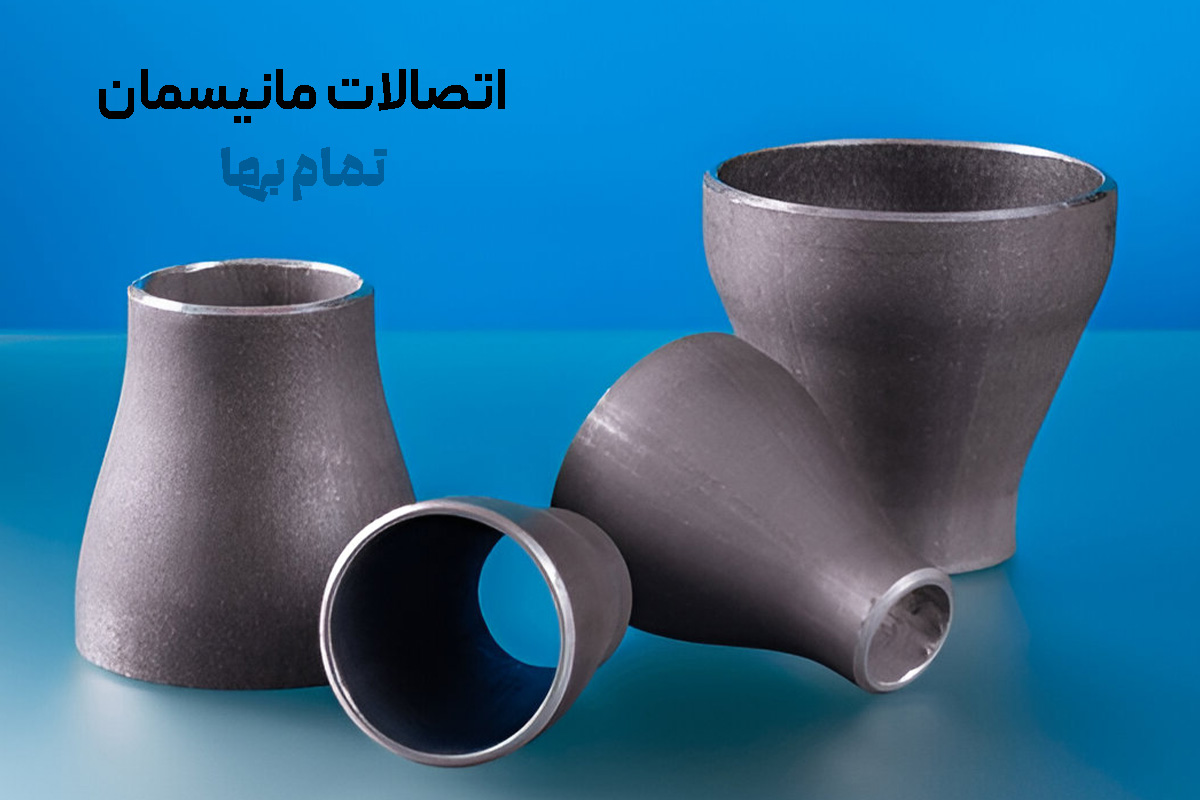
Seamless (Mannesmann) fittings are among the vital components of any advanced piping system; components that, thanks to their monolithic construction and the complete elimination of a weld seam, significantly raise the safety and efficiency of fluid lines. In the design and operation of high-pressure and high-temperature fluid transmission networks, seamless fittings in accordance with international standards such as ASME B16.9 and ASTM A234 are not only an engineering requirement but also a guarantee of the system’s long-term stability. Mannesmann fittings are produced in Schedules 20, 40, 80, 160, and even special API grades for crude-oil pipelines, with nominal diameters from ½ inch to 24 inches in industrial class and up to 36 inches in ultra-heavy projects. Precise selection of schedule and diameter depends directly on fluid type, design pressure, operating temperature, flow velocity, and allowable pressure drop; therefore, piping engineers always use pressure–temperature (P–T) charts to determine the most appropriate class.
Metallurgy and Chemical Composition
The base materials for Mannesmann fittings are commonly carbon steels A234 WPB, low-alloy chromium–molybdenum steels (such as A335 P11/P22 for high temperatures), and stainless steels in grades 304/316. In applications containing sour hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), NACE MR0175 requires that the chemical composition and heat treatment be selected so the part hardness does not exceed the allowable limit, reducing the risk of hydrogen cracking. In chloride environments, duplex alloys 2205 or superaustenitic 904L provide favorable resistance to pitting and stress corrosion cracking (SCC). Adding controlled amounts of Ni and Mo, while increasing cost, can multiply service life under severe corrosion.
Quality Control and Non-Destructive Testing
For each seamless fitting, a suite of tests is performed per the Quality Control Plan (QCP):
- Ultrasonic testing to ensure absence of internal cavities or radial cracks.
- Sectional radiography to verify thickness uniformity in critical zones.
- Hydrostatic testing, typically up to 1.5× the design pressure.
- PMI to match alloy grade with material certification.
- Charpy impact test at sub-zero temperatures for LNG lines or export lines in cold climates.
For critical lines, an EN 10204 3.2 certificate with third-party approval is usually issued and archived in the project document bank.
Manufacturing Methods and Technical Comparison
| Manufacturing method | Max economical diameter (in) | Dimensional accuracy | Microstructural uniformity | Production efficiency | Typical applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal casting | 30 | Medium | Very high | Medium | High-pressure boilers; furnace tubes |
| Hot extrusion | 14 | High | High | High | Industrial refrigeration; hydraulic lines |
| Spray forming | 18 | Medium | Good | Low | Special alloy parts; acid transfer |
| Ring forging & machining | 8 | Very high | Very high | Low | Instrumentation fittings; superalloy instrumentation lines |
Hydraulic Performance and Design Criteria
The loss coefficient (K) for elbows, tees, and reducers is critical in pipeline design. As bend radius increases, K decreases and pump/compressor energy consumption drops. A long-radius (LR) elbow with R/D = 1.5 typically yields ~30% lower pressure loss than a short-radius (SR) elbow with R/D = 1. In light-crude lines at 60 °C with low viscosity, using LR elbows not only reduces K but also lowers cavitation risk in suction pumps. Conversely, in the tight spaces of brown-field refineries, an SR elbow may be the only option, and the designer must increase pump power to compensate for the extra pressure drop.
Coatings and Corrosion Protection
For outdoor systems, common coatings include hot-dip galvanizing, three-layer epoxy (3LPE), and field-joint coating. Galvanized fittings are reliable only up to 200 °C; at higher temperatures, zinc can melt and create a hydrogen-embrittlement hazard. For seawater cooling lines, cement lining or a polyurethane sleeve at the weld is more effective. In sour-gas lines, continuous injection of a corrosion inhibitor inside the pipe and monitoring corrosion rate with an ER probe are essential to prevent iron-sulfide abrasives from gradually wearing fittings.
Schedule–Thickness–Allowable Pressure Correlation Table
| Schedule | NPS 4″ thickness (mm) | Allowable pressure at 38 °C (bar) for A106 Gr.B | Allowable pressure at 400 °C (bar) |
|---|---|---|---|
| STD (40) | 6.02 | 120 | 61 |
| XS (80) | 8.56 | 164 | 83 |
| 160 | 14.27 | 259 | 131 |
| XXS | 18.26 | 312 | 158 |
(Calculations based on ASME B31.3 with weld joint factor = 1.)
Installation Considerations, Preheating, and PWHT
Welding of carbon-steel seamless fittings is performed by SMAW or GTAW; for higher speed, GMAW is also accepted. For thicknesses above 19 mm, preheating up to 150 °C and maintaining it during welding are essential to prevent cold cracking. After completing the root pass and several cover passes, the QC inspector may request root approval with gamma-film radiography, minimizing rework risk in the final layers. In Cr–Mo steels, performing PWHT in the 650–700 °C range, holding one hour per 25 mm of thickness, is important to reduce residual stresses and restore toughness.
Application Examples in Industry
At Arak Refinery, replacement of 3,700 m of fittings in the furnace radiant row during the 1402 overhaul using WP9 seamless fittings extended design life by two operating cycles. In the South Pars export pipeline, 8″ Schedule 80 seamless fittings with 3LPE coating sustained 140 bar at 85 °C for 9 years without leakage. In the marine sector, Tidewater used 316L stainless fittings for OSV fuel systems to reduce chloride-induced pitting; periodic inspections show a corrosion rate under 0.01 mm/year.
Maintenance and Remaining Life Monitoring
In high-temperature environments, it is vital to determine MTTF via periodic UT thickness measurements and calculation of wall-thinning rate. If corrosion rate exceeds 0.4 mm/year, material selection or thickness should be revised for the next shutdown period. Using a condensate pot in steam lines, in addition to removing corrosive particles, reduces thermal fatigue of fittings.
Economic Indicators and Market
Global scrap steel prices and iron-ore rates are fundamental to raw steel pricing; in Iran’s market, the NIMA USD rate and slab import tariffs have the greatest impact. On average, material accounts for ~65% of a fitting’s total cost, energy 10%, labor 8%, and taxes/logistics 17%. In the first half of 1404, demand growth from southern desalination pipeline expansions and product-transfer schemes increased average prices of 6–12″ Mannesmann fittings by 18%; however, with new steelmaking units coming online, price growth is expected to moderate by year-end.
Safety Requirements and National Regulations
Based on Iran’s National Building Regulations, Chapter 16, seamless fittings are legally required in main risers of municipal gas and in Dry/Wet fire-fighting lines. The Ministry of Oil HSE code, clause 7-1, explicitly emphasizes that in process lines above 40 bar and 200 °C, installation of seamless butt-weld fittings or ring-joint flanges is mandatory. Non-compliance may lead to A-level risk classification and operations shutdown.
Complete Set of Fittings and Proper Selection
- 45° and 90° LR/SR elbows for quick changes in direction.
- Equal or reducing tees for branching with minimal turbulence.
- Eccentric or concentric reducers for lowering water hammer in pump stations.
- End caps for temporary or permanent line blanking.
- Threaded couplings and swage nipples to transition from welded to threaded systems in instrumentation lines.
- Crosses and nipples for distribution in fire-fighting networks.
All these parts, if produced by ring forging and final machining, will have a maximum dimensional tolerance of ±0.25 mm, simplifying field assembly.

Technical Recommendations When Purchasing
- Verify material certificate matches the heat number stamped on the part.
- Obtain hydrotest certificate with the manufacturer QC unit’s stamp and signature.
- In cold climates, request Charpy testing at −46 °C per ASME B31.3 Category 2.
- Spool numbering should allow accessible disassembly.
- For orders above 24″ in medium schedules, seamless manufacturing may be limited; in such cases either weld multiple smaller pieces or order a longitudinal-seam (long-seam) fitting per API 5L spec.
As one of the reputable suppliers of Mannesmann fittings in the Iranian market, “Tamam Baha” leverages a wide network of Iranian and international manufacturers such as Benkan and several European brands to meet the needs of oil, gas, petrochemical, and construction projects in the shortest possible time. While not the only supplier in the country, its competitive edge lies in pre-sales technical support, the ability to source custom sizes, and assurance of product authenticity via complete documentation of Heat Numbers and 3.1 certificates—minimizing the risk of delay or non-conformity for clients across Iran and neighboring regions.